Which Fluids are Best Measured with Transit-Time Ultrasound?
Fluids that have low ultrasound attenuation are great candidates for measuring flow via transit- time ultrasound. There are three main characteristics of fluids that have low ultrasound attenuation. They are:
1. No suspended particulates. These particles lead to a scattering effect on the 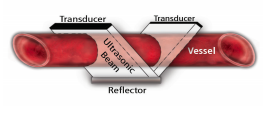 ultrasound waves, which impacts the measurement.
ultrasound waves, which impacts the measurement.
2. No air bubbles or pockets. These will lead to reflection of the ultrasound waves, which prevents an accurate flow measurement. However, due to this reflection phenomena, ultrasound can be a good way to detect when an air bubble (even very small bubbles, 5% of cross section volume) passes through the section of the flow path being monitored.
3. Laminar flow, especially any changes in flow profile from laminar to turbulent. These changes or turbulent flow can lead to refraction of the ultrasound waves, which, again, is observed as attenuation of the signal.
The most commonly measured fluids are water, ionic solutions and blood, all of which have relatively low ultrasound attenuation.



